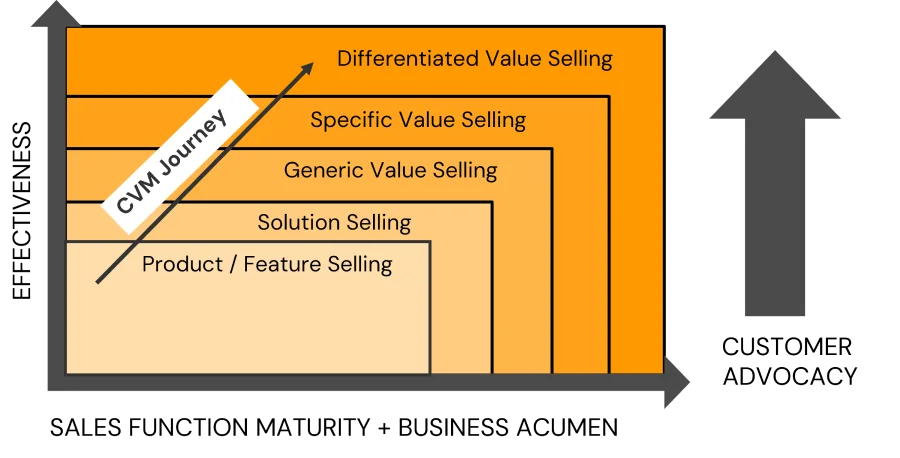
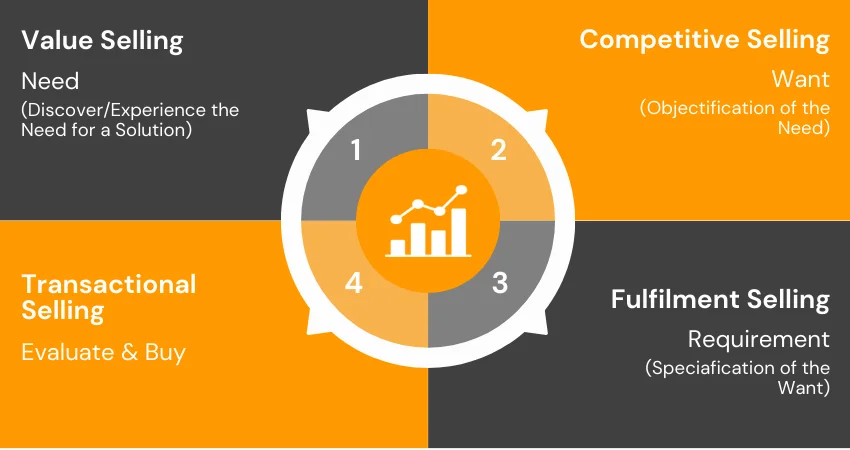
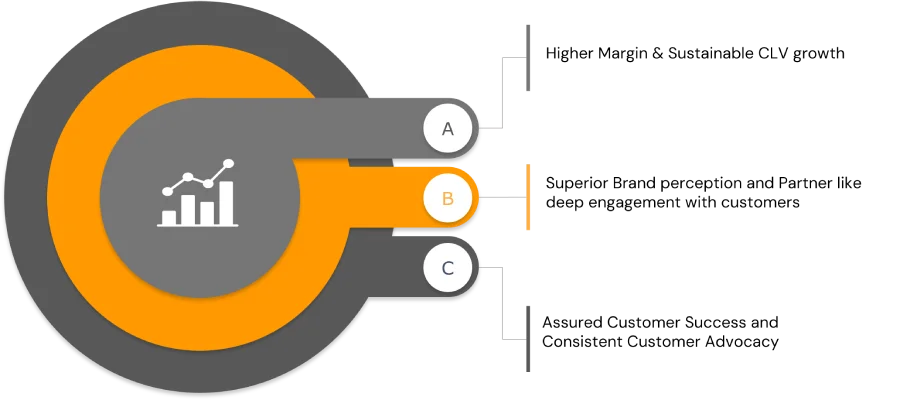
Ram is an IT industry veteran with over 3 decades of exemplary experience in various global leadership roles. He has a well-rounded profile with experience across Hardware, Software & Services business. He is conversant with a range of Enterprise applications across ERP, PLM & CRM – On Premise, On Demand & Cloud based solutions.
Ram possesses remarkable credibility & personal integrity that leaves lasting impressions with Corporate Decision Makers, Partners & Employees. He is comfortable & familiar with working in cross cultural environments across GEOs including India, Middle East and North America.
Starting his career as a Direct Field Sales rep in 1983, He enjoyed steady career progression over a 33 year span which led him to Sales & General Management roles in a wide spectrum of Indian and MNC organisations including Dassault Systemes (As VP – Business Transformation for South Asia), Oracle India & USA (As Senior Director – Sales, Inside Sales & Channel Management), Silicon Graphics Inc (As Large Account Manager), Gulf Computers (Sales Manager – Oil/Gas, Retail in UAE) & Wipro Infotech (As Regional Sales Manager).
He has managed annual revenues in excess of US$ 100 Million spanning several assignments. He has extensive People Management skillsin various functions such as Sales, Inside Sales, Presales Consultants, Marketing, Channel Sales Support & Post Sales Delivery teams.
Ram has a wide exposure across industries including Manufacturing, IT/BPO, Aerospace & Defence, Retail, Construction, Media, Life Sciences & Textile companies.
Some of his major skills set include:
- Formulating annual business plans / strategies
- Implementing business development plans, setting up sales objectives and designing / streamlining processes & systems to ensure smooth sales execution.
- Understanding clients business needs, strategic direction and identifying initiatives that will allow business to meet those strategic goals.
- Identifying and networking with prospective Greenfield clients as well as generating predictable business from install base accounts.
- Attracting, recruiting, on boarding & monitoring the performance of team members to ensure efficiency in sales operations and meeting of individual & group targets.
Ram graduated from Maharaja Sayajirao University, Baroda with a Bachelors’ in Electrical Engineering in 1981, followed by a MBA from Symbiosis Institute of Business Management, Pune in 1983. He continues his association with his alma mater, Symbiosis Institute in Bangalore as a member of the Advisory Board.
In his “second” innings, Ram is a Business Associate with a leading Tata group company and helps them with recruitment, training, and enablement. He also closely engaged with several other businesses as a Board member or in an Advisory capacity including Prumatech Infosystems and Digital Interact.
At Bizwin, Ram is a part of the core Leadership team that charts out the direction of the company’s growth, IP building, customer acquisition and delivery initiatives.
Mumbai born Ram has now adopted Bangalore as his home for the past 13 years and enjoys his leisure time with several activities including Travel to the Himalayas, Reading and Spirituality.